Contoh soal ini Saya dapat dari internet, sebuah soal dalam test untuk mendapatkan Certificate Functional Safety Expert. Biasanya soal terbagi 3 type, pilihan ganda, esai dan study kasus (desain).
Di sini saya hanya ambil soal study kasusnya saja, karena biasanya mempunyai bobot penilaian yang paling besar.
Agak sulit/rancu menerjemahkan soalnya dalam bahasa, mungkin lebih baik soalnya tetap dalam bahasa Inggris, untuk jawaban Saya coba terjemahkan, karena ada bebrapa kalkulasi/perhitungan.
Kasus :
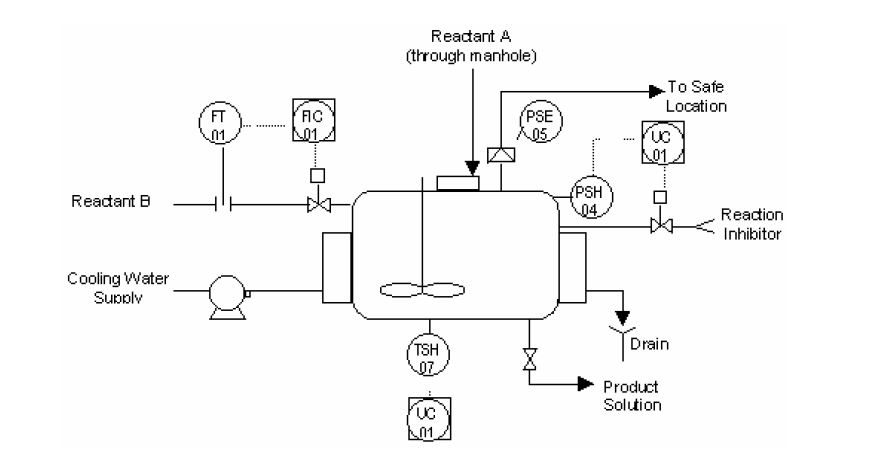
A specialty chemical company has developed a batch process to produce a new polymer. The process creates a solution of polymer and cyclohexane that is withdrawn from the bottom of the pressurized, water cooling jacketed, continuously stirred tank reactor. The vessel is charged by filling it with 250 kg. of cyclohexane and manually dumping 125 kg. or 5 bags of reactant A into the vessel. After the vessel is charged and closed, the stirring mechansim is started and the vessel's jacket is flooded with cooling water. After the stirring and cooling have been established a small, metered rate of 0.5 kg/min of reactant B is continuously added to the solution. Reactants A and B combine to form the desired product. Each batch operates for three weeks, and 5 batches are operated per year.
The reaction A and B is nearly instantaneous and highly exothermic. Safe operation of this process requires that cooling water continuously be flowing through the jacket. Hazard analysis determined that loss of cooling water could cause a "runaway" reaction and physical explosion of the vessel. The plant's safety division performed a quantitative consequence analysis of the physical explosion of this vessel. The analysis determined that the explosion would result in the following consequence:
- Probable Loss of Life: 5.64 fatalities
- Probable Injuries: 13.24 injuries
The following layers of protection were identified as a safeguard against explosion of the vessel due to runaway reaction.
- A rupture disk set to relieve the pressure well below the design pressure of the vessel
- Operator intervention to high vessel temperature, high vessel pressure, and low cooling water flow alarms
A safety instrumented system that injects a reaction-inhibiting chemical if the vessel temperature or pressure exceeds predetermined conditions was recommended in the process hazards analysis.
A process engineer determined the following frequencies and failure probabilities after reviewing the history of the plant.
- Cooling Water Pump Fails: 1/75 /year
- Rupture Disk PFD: 0.0956
- Operator Response to Cooling Water Loss pfd: 0.1
The plant uses the following table to determine tolerable frequency of an unwanted event, based on its consequence.
Soal :
1. Create a LOPA diagram that describes the situation defined above.
2. Quantify the LOPA to obtain the frequency at which the unwanted explosion is expected to
occur.
3. Based on the company's tolerable risk guidelines, select the safety integrity level for the
inhibitor injection SIS.
Jawaban :
1.
Pembuatan LOPA untuk menggambarkan Situasi dan kuantifikasi dalam menentukan frekuensi kecelakaan yang tidak diinginkan.
LOPA diagram yang di buat memiliki empat cabang dengan dua output.
Tahap pertama adalah kejadian awal, yang merupakan hilangnya air pendingin.
Cabang pertama, apakah kejadiannya pada saat operasional.
Cabang kedua mewakili apakah operator gagal untuk menanggapi atau tidak.
Cabang ketiga adalah apakah rapture disk gagal.
Lalu akhirnya adalah terjadi ledakan.
2. Plant ini tidak terus beroperasi, oleh sebab itu akan mengurangi frekuensi kejadian yang tidak diinginkan.
Plant operasional:
Dari hasil perhitungan di atas, dan data2 yang di berikan maka kemungkinan kejadian ledakan dapat di hitung :
probability pump fail * plant operational * Operator loss * rapture disk fail
0.0134 * 0.29 * 0.1 * 0.0956 = 0.00003715 = 3.7E-5
3. Karena jika terjadi ledakan (sesuai data dari soal) maka kemungkinan terjadi nya korban jiwa (Probability Lost Life) = 5.64 fatalities. Maka sesuai tabel tolerable frequency dan consequence di atas, maka kejadian ledakan ini di klasifikasikan sebagai Multiple Fatalities Likely.
Dan sesuai tabel tersebut juga, bahwa Multiple Fatalities Likely mempunya tolerable frequency 1.0E-6.
Dari data-data tersebut maka, kita dapat menentukan SIS PFD yang di butuhkan.
target PFD = 1.0E-6
event explosion probability = 3.7E-5
target PFD = event explosion probability * SIS PFD
SIS PFD = (1.0E-6) / (3.7E-5) = 2.7E-2
Risk Reduction Factor (RRF) dari SIS PFD = 1/(2.7E-2) = 37
Merujuk ke IEC 61511, RRF SIL 1 adalah 10 - 100, dan RRF SIL 2 adalah 100 - 1000.
Maka dapat di simpulkan SIS yang di buat harus SIL 2.